演算法筆記 - Binary Search Tree (BST)
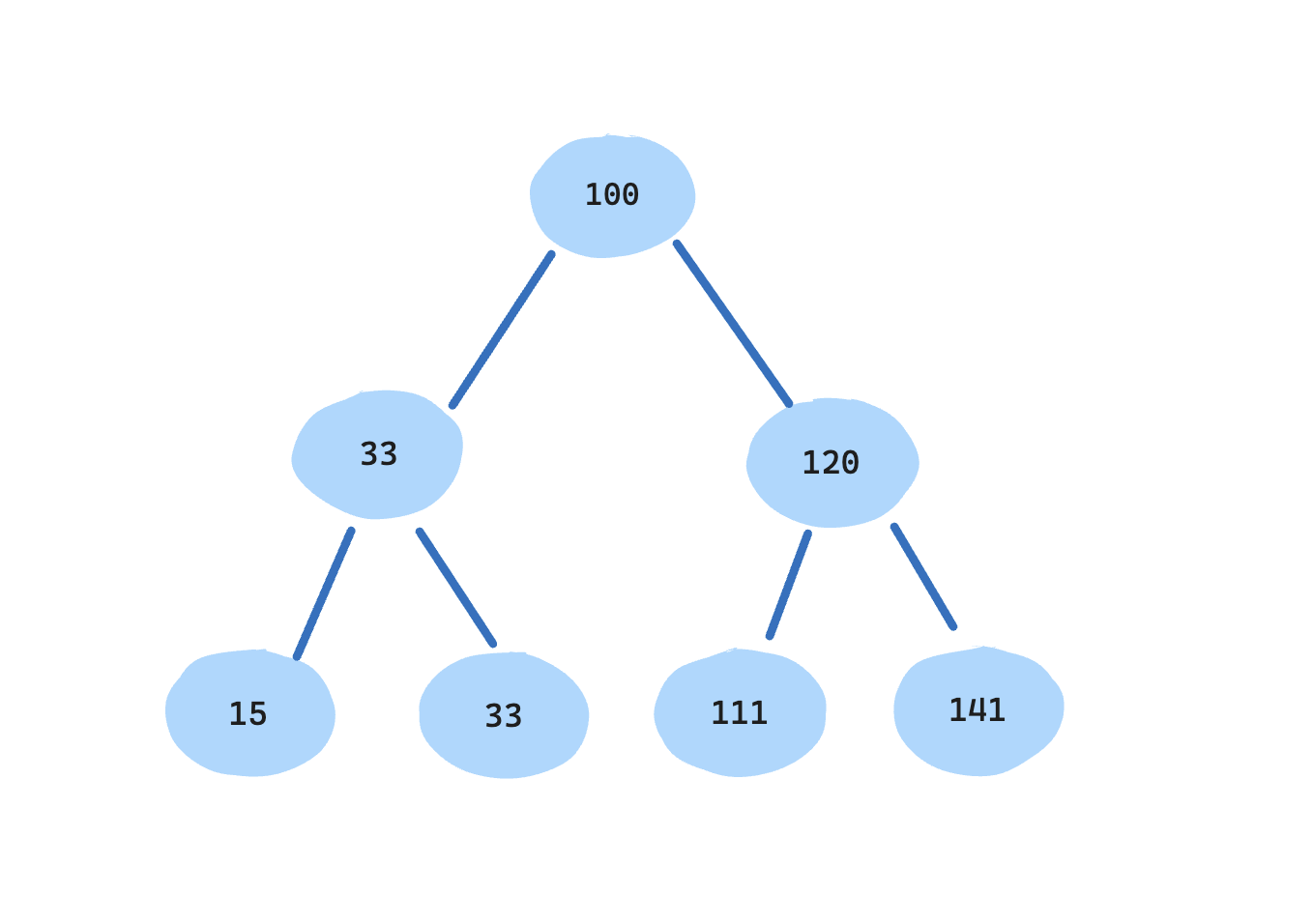
What’s a binary search tree?
二元搜尋樹是一種保留某種關係的二元樹,就如同名字講的,他很適合用來搜尋。一個 BST 必須符合這個條件,對於一個節點而言:
- 左子樹中所有節點的值小於該節點的值。
- 右子樹中所有節點的值大於該節點的值。
可以簡單理解為: 任何兩個節點,左邊那個節點的值一定大於右邊節點的值 。也因為這個條件,在 BST上搜尋數值會比在單純的陣列裡面逐個元素尋找還要迅速。在一個二元樹上,可以執行一些操作:
- 搜尋 (lookup)
- 新增 (insert)
- 刪除 (delete)
節點
「節點」(Node)就是樹裡面的每一個點,在程式裡面我們會用特定的結構來表示節點的值,以 JavaScript 為例的話就是:
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.value = value;
}
} 其中 left 表示左邊的子節點,而 right 代表右邊的子節點,value 則是節點本身的值。
現在讓我們來試著創造一個 BST ,我們會新增一個 class 上面有 lookup 、insert 、delete 三種方法,接著我們會個別實作它們。
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor(){
this.root = null;
}
insert(value){}
lookup(value){}
remove(value){}
}insert 新增
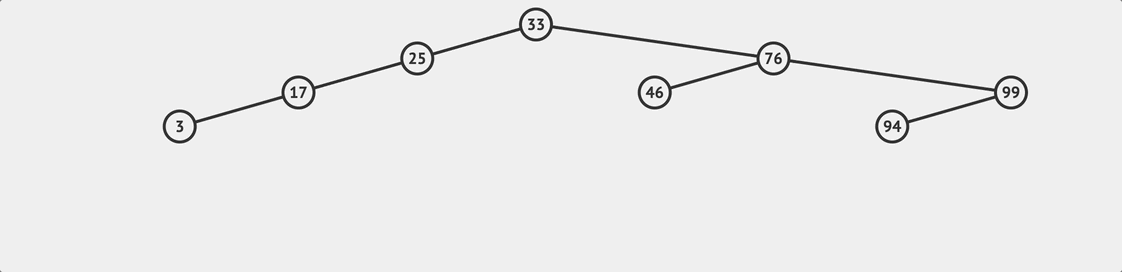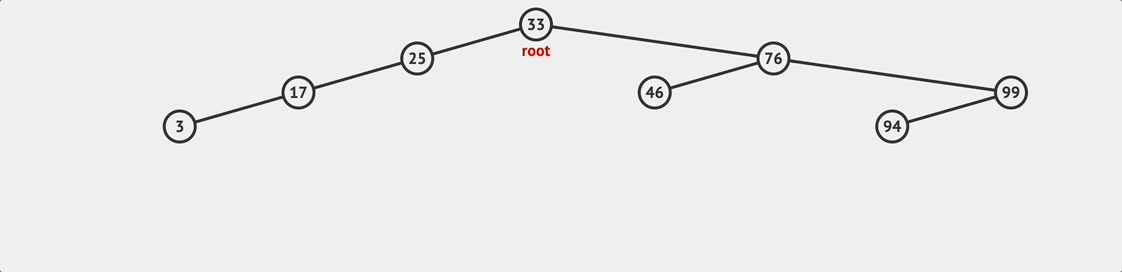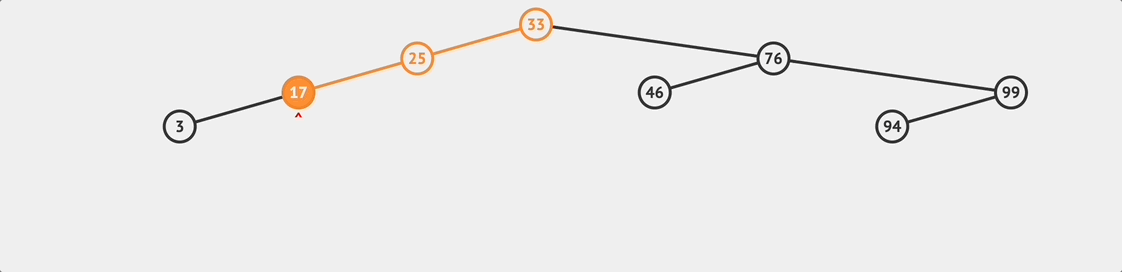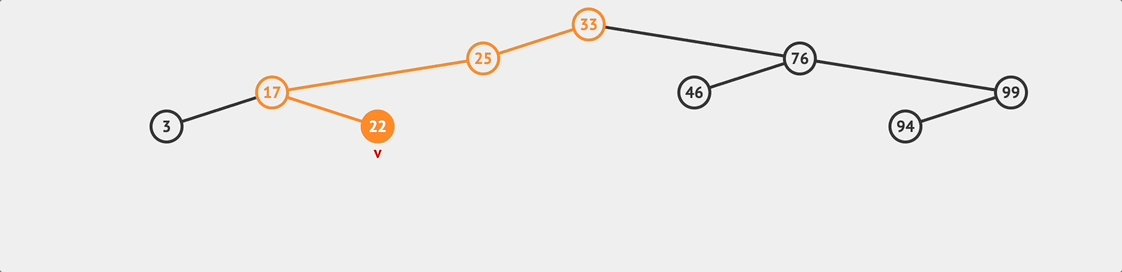 BST insert flow
BST insert flow insert(value){
// 新增節點
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode;
} else {
...
}
} 接著就可以開始根據 value 來尋找適合插入的位置,還記得 BST 的規則是什麼嗎?任何兩個節點,左邊那個節點的值一定大於右邊節點的值。我們會從根節點遍歷往下尋找,判斷目標值 value 是大於或小於目標節點的值,如果結果是大於,就往右邊繼續比較和查找;否則往左邊。執行這樣的邏輯直到找到適合插入的位置為止。
insert(value){
// 新增節點
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode;
} else {
// 先把要檢查的目標 node 設為 root
let currentNode = this.root;
while(true){
// 拿要插入的節點的值與當下節點的值作比較
// 如果目標值小於當下節點的值,就往左邊找
if(value < currentNode.value){
// 先檢查左邊的值存不存在
if(!currentNode.left){
// 如果不存在,表示這個位置就是目標位置
currentNode.left = newNode;
return this;
}
// 如果左邊還有值,表示可以往下尋找
currentNode = currentNode.left;
} else {
// 如果目標值大於當下節點的值,就往右邊找
// 右邊的邏輯比照上面
if(!currentNode.right){
currentNode.right = newNode;
return this;
}
currentNode = currentNode.right;
}
}
}
}loopup 查找
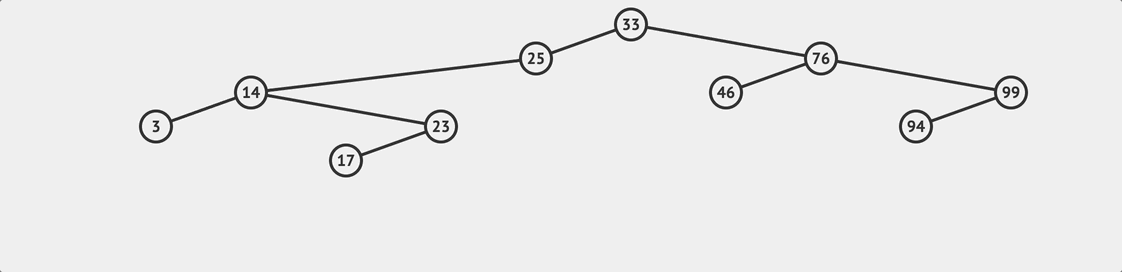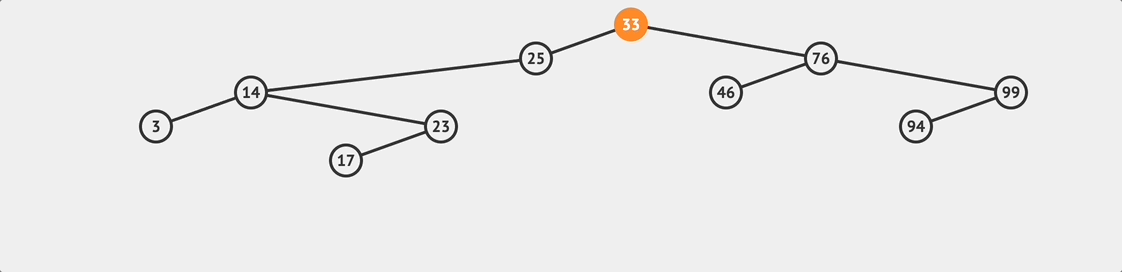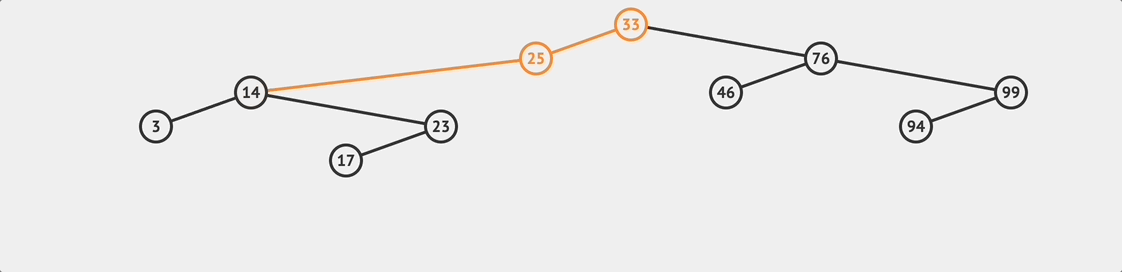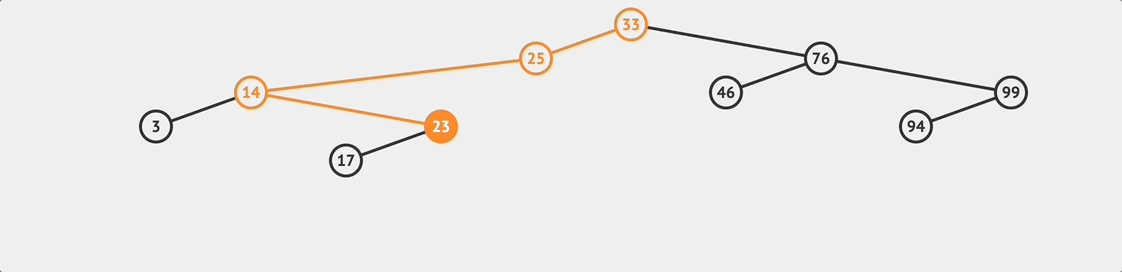 BST loopup flow
BST loopup flow 要注意的是如果查找到最後發現 currentNode 變成 null ,那就表示想要查找的值並不存在這棵樹上。
...
lookup(value){
if (!this.root) {
return false;
}
let currentNode = this.root;
while(currentNode){
if(value < currentNode.value){
currentNode = currentNode.left;
} else if(value > currentNode.value){
currentNode = currentNode.right;
} else if (currentNode.value === value) {
return currentNode;
}
}
return null
}
...remove 刪除
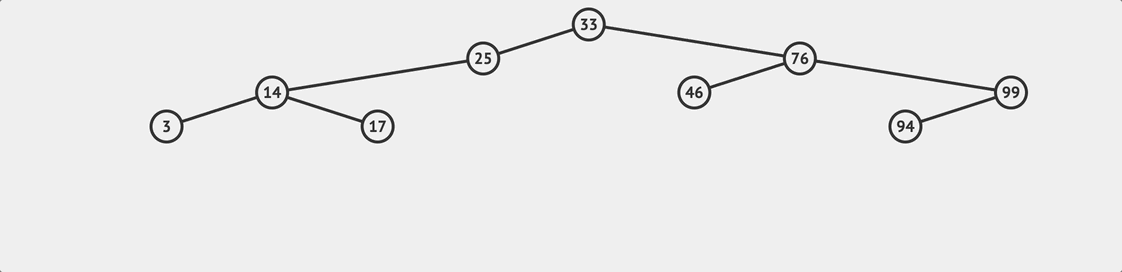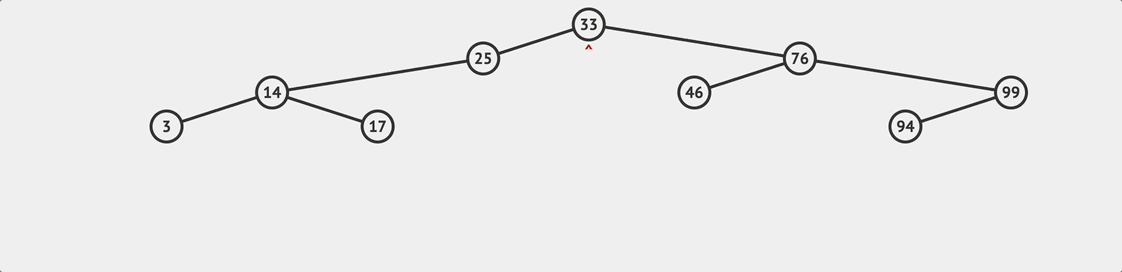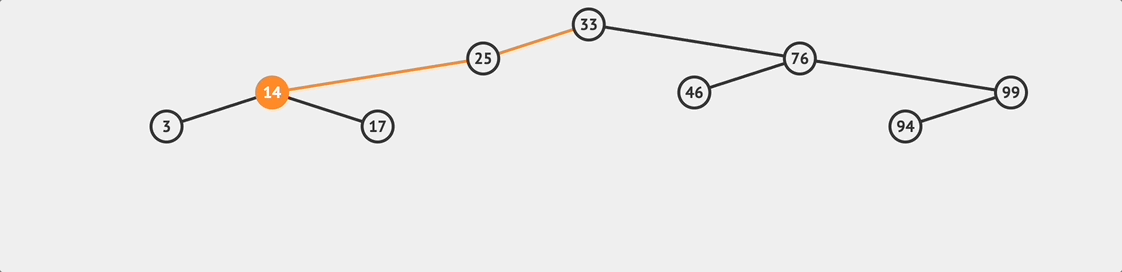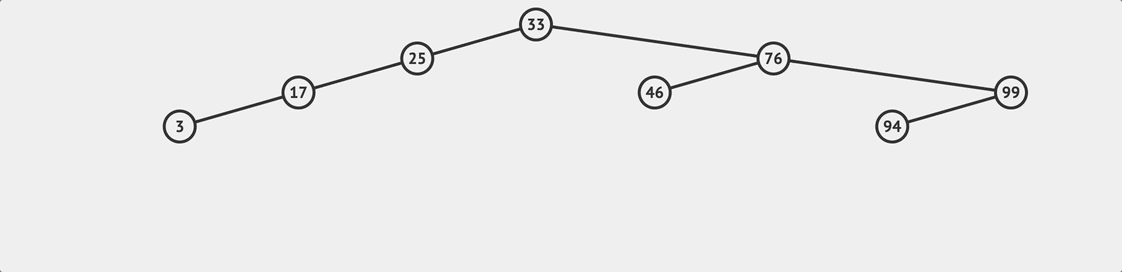 BST remove flow
BST remove flow - 查找要被刪除的目標節點
- 移除這個節點
第二點要注意的是如果我們刪除的目標節點是有其他子節點的,那麼我們必須在這個節點被移除後 把剩下的子節點和原來的樹接回在一起 ,就像上面流程圖展示的流程一樣。
所以在查找的過程中,除了在搜尋時我們會不斷修改 currentNode 用來執行下一次的數值大小判斷,我們還必須把我們 正在查找的節點的父節點 (Parent Node) 也一起記下來 ;ˋ至於搜尋的流程,基本上跟前面提到的 lookup 的邏輯一樣。
remove(value) {
if (!this.root) {
return false;
}
let currentNode = this.root;
let parentNode = null;
while (currentNode) {
// 和查找邏輯一樣
if (value < currentNode.value) {
parentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.left;
} else if (value > currentNode.value) {
parentNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.right;
} else if (currentNode.value === value) {
...
// 找到目標節點
// 核心刪除邏輯
}
}
} 接下來就進入到主要的刪除邏輯,實作上可以有不同的做法,以下我會用其中一種來說明。需首先我們要考慮到以下三個情況(這邊一樣用 currentNode 來表示當下正在查看的節點) :
1. currentNode 沒有右邊子節點
這是最單純的狀況,如果 A 節點只有左邊節點B的話,那表示節點 A 被刪除之後只要考慮 B 是要被指派到它的上層節點的左節點或右節點。
2. currentNode 有一個沒有左子節點的右子節點
如果 currentNode 有左子節點,而且有一個 沒有左子節點的右子節點 ,那在 currentNode 被刪除之後,我們會讓右子節點接管,然後把原來 currentNode 的左子節點移動到右子節點的左子節點。
3. currentNode 有一個有左子節點的右子節點
如果目標節點右子節點有左子樹的話,我們就要找到在這個左子樹上的最小值(最左子節點),然後讓這個最左子節點取代原來的節點,換句話說我們要找 一個比原來節點大,但是比其右節點上數值都要小的值 。
remove(value) {
...
// } else if (currentNode.value === value) {
...
// 找到目標節點
// 核心刪除邏輯
// 1. currentNode 沒有右邊子節點
if (currentNode.right === null) {
if (parentNode === null) {
// 如果沒有 parentNode 表示是 root
this.root = currentNode.left;
} else {
// 比較當前節點的值和 parentNode
// 如果上層節點比較大,那麼就把 currentNode.left 指派成上層節點的左子節點
if (currentNode.value < parentNode.value) {
parentNode.left = currentNode.left;
// 反之則指派成右子節點
} else if (currentNode.value > parentNode.value) {
parentNode.right = currentNode.left;
}
}
// 2. currentNode 有一個沒有左子節點的右子節點
} else if (currentNode.right.left === null) {
// 原來 currentNode 的左子節點在 currentNode 被刪除後將成為右子節點的左子節點,然後由這個右子節點接管 currentNode
currentNode.right.left = currentNode.left;
if (parentNode === null) {
this.root = currentNode.right;
} else {
// 接合被刪除節點的子節點樹,與前一個情況相同
if (currentNode.value < parentNode.value) {
parentNode.left = currentNode.right;
} else if (currentNode.value > parentNode.value) {
parentNode.right = currentNode.right;
}
}
// 3. currentNode 有一個有左子節點的右子節點
} else {
//先找到右子樹上的最左子節點
let leftmost = currentNode.right.left;
let leftmostParent = currentNode.right;
while (leftmost.left !== null) {
leftmostParent = leftmost;
leftmost = leftmost.left;
}
// 如果最左節點有右子樹,把他指派給其上層節點
leftmostParent.left = leftmost.right;
// 把最左節點的左右節點接上 currentNode 的左右節點
leftmost.left = currentNode.left;
leftmost.right = currentNode.right;
if (parentNode === null) {
this.root = leftmost;
} else {
// 判斷原來節點的值是比其上層節點大或小
// 以此決定新的節點要接上上層節點的左節點或是右節點
if (currentNode.value < parentNode.value) {
parentNode.left = leftmost;
} else if (currentNode.value > parentNode.value) {
parentNode.right = leftmost;
}
}
}
}
}
}