How to make a Hash Table in JavaScript
This is a note about Hash Table in JavaScript that I wrote when I was learning it.
What’s Hash Table? Hash Table is a data structure that stores key-value pairs and allows us to find the corresponding data quickly using the key we input.
Hash Table is often used in JavaScript, but we don’t know it.
For example, Set and Map, and even Object are using the concept of Hash Table.
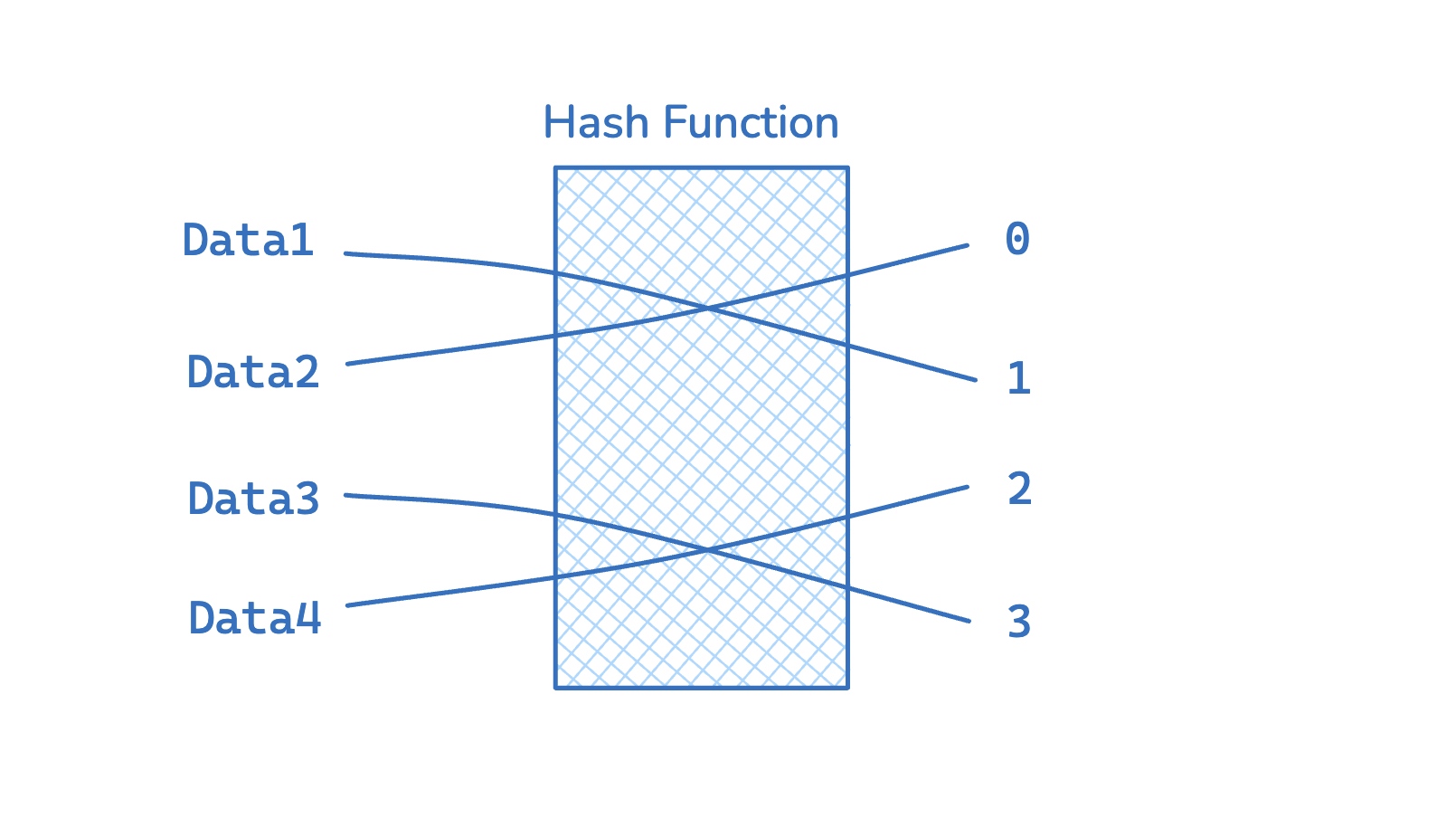
Here is an example of a Hash Table structure ( image source ):
 Hash Table Structure
Hash Table Structure You can see the key is on the left-hand side part, and the corresponding value is on the right-hand side; and there is a Hash Function in the middle, which is used to put each different value into a different position on the table. It will calculate the position (index) on the Hash Table based on the key you input, the value returned by the Hash Function should remain the same as long as the input value is the same.
Hash Function
In this article, we will focus on implementing the entire Hash Map, so the Hash Function is not the core part.
Here is a simple implementation of the Hash Function:
function simpleHashKey(key, arraySize) {
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
hash += key.charCodeAt(i); // add the Unicode value of each character
}
return hash % arraySize; // ensure the result is lower than or equal to the array size
}
const arraySize = 10;
console.log(simpleHashKey("abc", arraySize)); // 6
console.log(simpleHashKey("xyz", arraySize)); // 8
console.log(simpleHashKey("a", arraySize)); // 7
HashTable Class
Then we can integrate this function into the HashTable class, and we also need set / get to add and find data, and keys to query all the keys in the Hash Table:
class HashTable {
constructor(size){
this.data = new Array(size);
}
_hash(key) {
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % size;
}
set (){}
get (){}
keys(){}
}set Function
To implement the set function, we need to do two steps:
-
there will be a parameter
key, use the Hash Function to find the corresponding storage position (Index) in the Hash Table -
store the value in the Hash Table, but we have to consider the Hash Collision
Hash Collisions
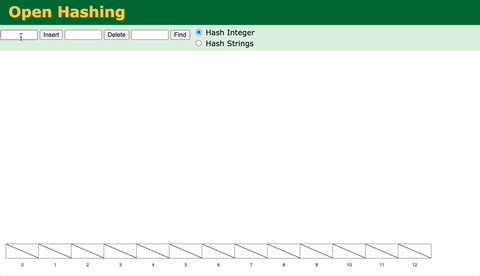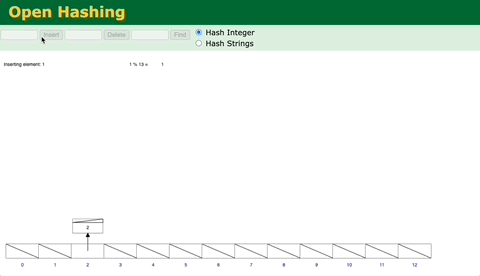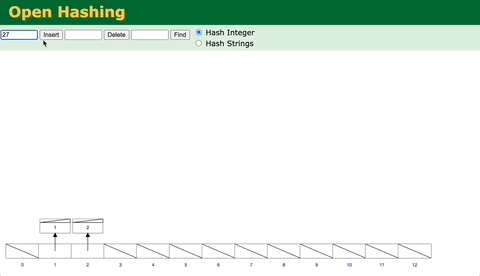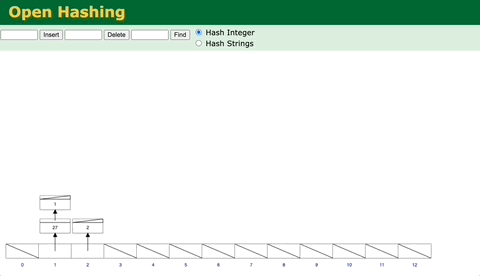 Hash Collisions
Hash Collisions So what is Hash Collision? It means when two different keys, after being calculated by the Hash Function, get the same Index. This may lead to data being overwritten and lost. There are many ways to solve this problem , the most common one is to use a LinkedList to ensure that multiple data can correspond to the same Index.
We’ll use a simpler Array to achieve the same purpose, and we will store the key and value in this Array:
 Our Hash Table Structure
Our Hash Table Structure By this way, the data in the Hash Table will always be an Array, so we can store the key and value in this Array to avoid the problem of data being overwritten due to collisions:
set(key, value) {
let address = this._hash(key);
if (!this.data[address]) {
this.data[address] = []; // if the address is empty, create an array
}
this.data[address].push([key, value]);
return this.data;
}get Function
If we want to get the data corresponding to a certain key, we need to use the key value to calculate the corresponding position through the Hash Function.
And if there is data stored in this position, we will get an array,
then we just need to find if the key we want to query is stored in this Array, and return the corresponding data:
get(key) {
let address = this._hash(key);
const bucket = this.data[address]; // get the array corresponding to the address
if (bucket) {
// traverse the array & find the corresponding key
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
if (bucket[i][0] === key) {
return bucket[i][1]; // return the corresponding value
}
}
}
return
}
...
keys Function
This function is used to query all the keys stored in the Hash Table, through implementing this function, we can also see a disadvantage of the Hash Table. That is when we want to visit all the values stored in the Hash Table, in order to avoid ignoring the values that are stored in the same position due to collisions, we need a second layer of for loop to query each one.
...
keys() {
const keysArray = [];
// traverse the entire data structure
for (let i = 0; i < this.data.length; i++) {
if (this.data[i] && this.data[i].length) {
// if the address has value, traverse each key-value pair
for (let j = 0; j < this.data[i].length; j++) {
keysArray.push(this.data[i][j][0]); // the last [0] is used to get the key
}
}
}
return keysArray;
}
... We’ve implemented the basic Hash Table, and usually HashTable also has other methods like delete and values, but the above three methods have covered the basic concepts of Hash Table, so we won’t go into details here.
Here is the complete code of the Hash Table:
class HashTable {
constructor(size) {
this.data = new Array(size);
}
_hash(key) {
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % this.data.length;
}
set(key, value) {
let address = this._hash(key);
if (!this.data[address]) {
this.data[address] = [];
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.data[address].length; i++) {
if (this.data[address][i][0] === key) {
this.data[address][i][1] = value;
return this.data;
}
}
this.data[address].push([key, value]);
return this.data;
}
get(key) {
let address = this._hash(key);
const bucket = this.data[address];
if (bucket) {
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
if (bucket[i][0] === key) {
return bucket[i][1];
}
}
}
return undefined;
}
keys() {
const keysArray = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.data.length; i++) {
if (this.data[i]) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.data[i].length; j++) {
keysArray.push(this.data[i][j][0]);
}
}
}
return keysArray;
}
}
const myHashTable = new HashTable(10);
...